Hedge fund strategy performance and definitions
Arbitrage – returned 0.34% in June 24, bringing 12-month performance to 3.67% and five-year CAR to 4.68%
Definition: Strategies that look to benefit from mispricings of the same instrument/asset or extremely closely related instrument. The strategy covers the following areas: convertible bond arbitrage, tail protection, volatility or opportunistic trades in this area, including but not limited to other areas such as capital structure arbitrage, ETF arbitrage or arbitrage of other closely related instruments.
Arbitrage – Convertible bond (CB)
Arbitrage – Tail protection (Tail)
Arbitrage – Volatility arbitrage (Vol)
Arbitrage – Opportunistic (Opp)
Arbitrage hedge fund performance
Latest strategy performance chart packs:
NET RETURN (12M)
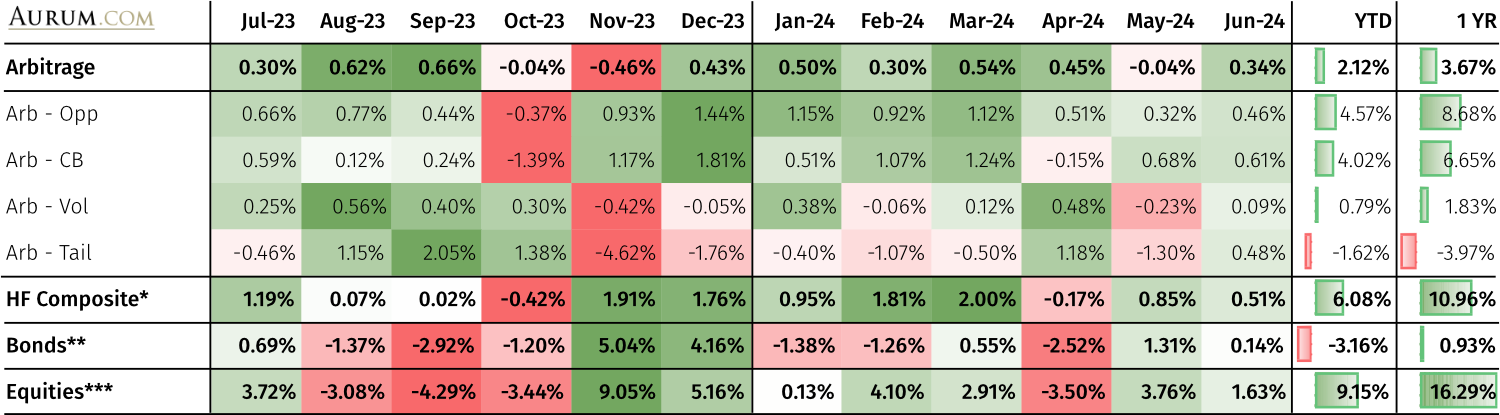
*HF Composite = Aurum Hedge Fund Data Engine Asset Weighted Composite Index. **Bonds = S&P Global Developed Aggregate Ex Collateralized Bond (USD). ***Equities = S&P Global BMI.
Want to share our charts? We are happy for you to do so, but please do quote the source: Aurum Research Limited’s Hedge Fund Data Engine
Credit – returned 0.64% in June 24, bringing 12-month performance to 10.10% and five-year CAR to 4.83%
Definition: Strategies that focus the vast majority of their trading on debt instruments, or instruments that are far more ‘debt-like’ in nature.
Credit – Credit RV (RV)
Credit – Direct Lending (Dir Len)
Credit – Distressed Credit (Distress)
Credit – Multi-Credit (Multi)
Credit – Municipal Credit (Muni)
Credit – Structured Credit (Struct)
Credit – Structured Credit LO (StrucLO)
Credit hedge fund performance
Latest strategy performance chart packs:
NET RETURN (12M)

*HF Composite = Aurum Hedge Fund Data Engine Asset Weighted Composite Index. **Bonds = S&P Global Developed Aggregate Ex Collateralized Bond (USD). ***Equities = S&P Global BMI.
Want to share our charts? We are happy for you to do so, but please do quote the source: Aurum Research Limited’s Hedge Fund Data Engine
Equity long/short – returned 1.19% in June 24, bringing 12-month performance to 13.66% and five-year CAR to 7.27%
Definition: Investing in global stocks, both on the long and short side. Most funds have a fundamental bias, value and/or growth oriented investment theses are typically adopted. Some managers may also be more tactical/technical in their approach, taking into account flows, positioning on the street and market dynamics as part of the investment decision making process.
US equity long/short (US)
Asia Pacific equity long/short (APAC)
European equity long/short (EUR)
Global equity long/short (Global)
Fundamental equity market neutral (FEMN)
Sector long/short (Sector)
Other long/short (Other)
Equity long / short hedge fund performance
Latest strategy performance chart packs:
NET RETURN (12M)

*HF Composite = Aurum Hedge Fund Data Engine Asset Weighted Composite Index. **Bonds = S&P Global Developed Aggregate Ex Collateralized Bond (USD). ***Equities = S&P Global BMI.
Want to share our charts? We are happy for you to do so, but please do quote the source: Aurum Research Limited’s Hedge Fund Data Engine
Event driven – returned -0.13% in June 24, bringing 12-month performance to 10.93% and five-year CAR to 7.37%
Definition: Broad strategy category covering funds that invest in securities of companies facing announced and anticipated corporate events. This includes, but is not limited to: M&A, Spin-offs, Company restructurings, some distressed situations (although if this is the dominating part of the strategy it will be classified as ‘credit-distressed’). The strategy identifies mispriced securities with favourable risk/reward characteristics based upon differentiated views of value-unlocking catalysts, event-probabilities and post-event valuations.
Event driven – Activist (Activist)
Event driven – Merger arbitrage (M&A)
Event driven – Multi-strategy (Multi)
Event driven – Opportunistic (Opp)
Event driven hedge fund performance
Latest strategy performance chart packs:
NET RETURN (12M)

*HF Composite = Aurum Hedge Fund Data Engine Asset Weighted Composite Index. **Bonds = S&P Global Developed Aggregate Ex Collateralized Bond (USD). ***Equities = S&P Global BMI.
Want to share our charts? We are happy for you to do so, but please do quote the source: Aurum Research Limited’s Hedge Fund Data Engine
Long biased – returned 0.62% in June 24, bringing 12-month performance to 11.32% and five-year CAR to 5.71%
Definition: Long only or overwhelmingly long-biased strategies. Covers multiple asset classes.
Long biased – Equities (Equity)
Long biased – Diversified growth (Div Growth)
Long biased – Commodities (Commods)
Long biased – Other (Other)
Long biased investing, which does not readily fit into the other classification taxonomy.
Long biased hedge fund performance
Latest strategy performance chart packs:
NET RETURN (12M)

*HF Composite = Aurum Hedge Fund Data Engine Asset Weighted Composite Index. **Bonds = S&P Global Developed Aggregate Ex Collateralized Bond (USD). ***Equities = S&P Global BMI.
Want to share our charts? We are happy for you to do so, but please do quote the source: Aurum Research Limited’s Hedge Fund Data Engine
Macro – returned -0.18% in June 24, bringing 12-month performance to 8.71% and five-year CAR to 5.24%
Definition: Macro funds take positions (can be either directional or relative-value) in currencies, bonds, equities and commodities, based on fundamental and qualitative judgements. Investment decisions can be based on a manager’s top-down views of the world (e.g. views on economy, interest rates, inflation, government policy or geopolitical factors). Relative valuations of financial instruments within or between asset classes can also play a role (or be the dominant part) in the investment process. Primary areas of focus are the liquid instruments of G10 countries, although they may also include emerging markets.
Macro – Fixed income relative value (FIRV)
Macro – Commodities (Commods)
Macro – Global macro (Global)
Macro – Emerging markets
(EM)
Macro hedge fund performance
Latest strategy performance chart packs:
NET RETURN (12M)

*HF Composite = Aurum Hedge Fund Data Engine Asset Weighted Composite Index. **Bonds = S&P Global Developed Aggregate Ex Collateralized Bond (USD). ***Equities = S&P Global BMI.
Want to share our charts? We are happy for you to do so, but please do quote the source: Aurum Research Limited’s Hedge Fund Data Engine
Multi-strategy – returned 0.89% in June 24, bringing 12-month performance to 10.79% and five-year CAR to 10.52%
Definition: A hedge fund where the capital is deployed across multiple sub-strategies and asset classes. Funds are typically extremely diversified and employ multiple PMs/risk taking groups.
Multi-strategy hedge fund performance
Latest strategy performance chart packs:
NET RETURN (12M)

*HF Composite = Aurum Hedge Fund Data Engine Asset Weighted Composite Index. **Bonds = S&P Global Developed Aggregate Ex Collateralized Bond (USD). ***Equities = S&P Global BMI.
Want to share our charts? We are happy for you to do so, but please do quote the source: Aurum Research Limited’s Hedge Fund Data Engine
Quant – returned 0.03% in May 24, bringing 12-month performance to 10.01% and five-year CAR to 4.82%
Definition: Systematic strategies: Funds trade securities based strictly on the buy/sell decisions of computer algorithms. Quant strategies primarily fall into the following categories: Quantitative equity market neutral, Statistical arbitrage, Quant macro/GAA (Global asset allocation), CTA, and risk-premia.
Quant – CTA (CTA)
Quant macro / GAA
(Macro)
Quant – Multi-strategy (Multi)
Quant – Statistical arbitrage (Stat Arb)
Quant – Quant equity market neutral (EMN)
Quant – Risk premia (RP)
Quant hedge fund performance
Latest strategy performance chart packs:
NET RETURN (12M)

*HF Composite = Aurum Hedge Fund Data Engine Asset Weighted Composite Index. **Bonds = S&P Global Developed Aggregate Ex Collateralized Bond (USD). ***Equities = S&P Global BMI.
Want to share our charts? We are happy for you to do so, but please do quote the source: Aurum Research Limited’s Hedge Fund Data Engine
Crypto
Definition: Focusing on investments in digital assets. These strategies can be implemented as long-only, long/short or market neutral with discretionary or quantitative approaches. Multi-strategy digital asset hedge funds also exist, and most funds implement a hybrid of strategies.
Source: Aurum’s proprietary Hedge Fund Data Engine database containing data on around 3,400 active hedge funds representing around $3.0 trillion of assets as at June 2024. Information in the database is derived from multiple sources including Aurum’s own research, regulatory filings, public registers and other database providers. Performance in the above chart is asset weighted. Box size reflects the AUM of the hedge fund industry, as tracked by Aurum. See the disclaimer for further details.
Bond and equity indices
The S&P Global BMI and S&P Global Developed Aggregate Ex Collateralized Bond (USD) Total Return Index (the “S&P Indices”) are products of S&P Dow Jones Indices LLC, its affiliates and/or their licensors and has been licensed for use by Aurum Research Limited. Copyright © 2021 S&P Dow Jones Indices LLC, its affiliates and/or their licensors. All rights reserved. Redistribution or reproduction in whole or in part are prohibited without written permission of S&P Dow Jones Indices LLC. For more information on any of S&P Dow Jones Indices LLC’s indices please visit www.spdji.com. S&P® is a registered trademark of Standard & Poor’s Financial Services LLC and Dow Jones® is a registered trademark of Dow Jones Trademark Holdings LLC. Neither S&P Dow Jones Indices LLC, Dow Jones Trademark Holdings LLC, their affiliates nor their third party licensors make any representation or warranty, express or implied, as to the ability of any index to accurately represent the asset class or market sector that it purports to represent and neither S&P Dow Jones Indices LLC, Dow Jones Trademark Holdings LLC, their affiliates nor their third party licensors shall have any liability for any errors, omissions, or interruptions of any index or the data included therein. By accepting delivery of this Paper, the reader: (a) agrees it will not extract any index values from the Paper nor will it store, reproduce or further distribute the index values to any third party for any purpose in any format or by any means except that reader may store the Paper for its personal, non-commercial use; (b) acknowledges and agrees that S&P own the S&P Indices, the associated index values and all intellectual property therein and (c) S&P disclaims any and all warranties and representations with respect to the S&P Indices.








